Much of the food we consume in our daily lives is industrialized, processed and ready-made. Only those who have a healthier diet end up taking precautions and doing a process that involves a reconnection with food. This is what living cooking proposes, which tries to consume food in a more natural way.
In practice, this presents a challenge. We are so used to cooking, frying and grilling that we don't even imagine and know what a food's true flavor is without going through any process before it reaches our plate.
Also called raw food, live cooking was born in the US in the 1980s. Today, there are already several people who are adept at this type of food. Check out the benefits of living cooking.
Benefits of live food?
- It is more nutritious;
- It is considered an alkaline diet;
- Helps with calorie control and weight loss;
- It is a source of vitamins;
- It detoxifies cells and tissues;
What is the purpose of living cooking?
 People who defend this type of preparation claim that foods, when cooked, lose nutrients and, thus, do not bring the same benefits to our body as when they were raw.
People who defend this type of preparation claim that foods, when cooked, lose nutrients and, thus, do not bring the same benefits to our body as when they were raw.
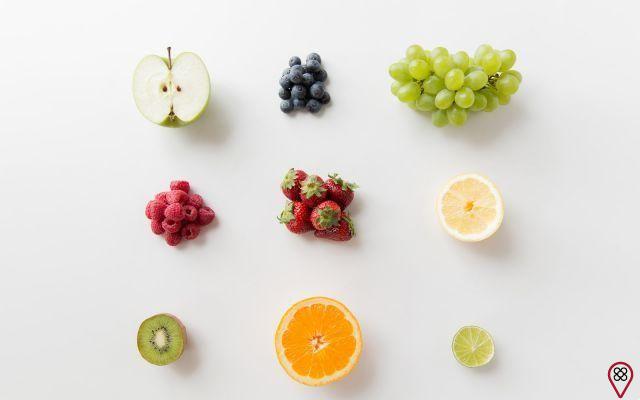
Of course, we cannot be radical. If you are interested in live cooking, you need to gradually introduce this type of food into your menu and, of course, consult a nutritionist. Live food is based on raw foods, fresh or dehydrated fruits, vegetables, seeds, sprouted grains or sprouts such as wheat, rice, barley, among others. Check out a live cooking menu below:
- Main fruits – Lemon, apples, oranges, avocados, bananas and green coconut.
- Vegetable - Kale, spinach, lettuce, cucumber, celery, parsley, zucchini, onion, tomato and peppers.
- herbs - Mint, basil, rosemary, oregano.
- Oilseeds – Walnuts, Brazil nut, almond, macadamia, pumpkin seed, sunflower, linseed and chia. (It is recommended to let them all soak for 4 hours and then dehydrate for another 8 hours to eliminate fungi and anti-nutritional factors).
- Grains – Buckwheat, common wheat, lentils, chickpeas.
- Vegetable butters – Sesame, almond and chestnut butters.
- oils - Olive oil, linseed oil, extra virgin coconut oil, unroasted sesame oil
- Sais – Himalayan pink salt and Celtic salt.
- Condiments – Balsamic vinegar, apple cider vinegar, soy sauce, miso.
- Spices - Curry, Turmeric, Turmeric, Ginger, Pepper, Garlic Powder, Nutmeg, Dried Ginger.
- Dry fruits - Plums, apricots and dates.
- Natural sweeteners – Agave, stevia.

Recipe for a live food:
fake rice
Ingredients:
- 1 carrot;
- 1 cauliflower;
- celery leaves to taste;
- 1 green pepper;
- 1 yellow pepper;
- 1 red pepper;
- 1 tablespoon of agave;
- 2 tablespoons of extra virgin olive oil;
- 1 tablespoon of soy sauce;
- 1 tablespoon of apple cider vinegar;
- Soybean paste (miso);
- Pepper to taste.
Preparation:
- Clean the cauliflower, pass it through the food processor and beat it lightly, taking care not to leave it like a porridge, and reserve;
- Grate the carrot. Cut the celery leaves and peppers into very small pieces;
- Mix everything with the cauliflower;
- Add the agave, extra virgin olive oil, soy sauce, apple cider vinegar, soy paste and pepper to taste in a bowl and mix well;
- To combine with the mixture of the cauliflower and to serve.
Text written by Angélica Fabiane Weise from the Eu Sem Fronteiras Team.